Tips for Maintaining Variable Geometry Turbochargers
As the trucking industry continues to change rapidly, some things remain constant. Efficiency, near zero emissions and fuel economy continue to be key issues for fleets and independent operators. Aerodynamics, organizing routes more accurately and thinner oils and engine improvements are just some of the ways the industry is responding to reduce fuel costs and help the environment. One component that can have an impact on performance in these areas is the turbocharger.
The use of Variable Geometry Turbochargers (VGT) is now standard on heavy duty and medium duty truck engines. Older wastegate actuator turbochargers were generally controlled by pressure or vacuum and operated basically as an on/off device.
Today’s heavy- and medium-duty engines incorporate electronically controlled variable geometry turbo. These new advanced turbochargers provide improved response across wider operating ranges (engine speeds), improved engine performance, fuel economy, enhanced engine braking, and provide a quicker engine deceleration for quicker shifting than fixed geometry (older wastegate) turbochargers. In addition, they allow for smaller engine displacements with increased horsepower and torque ratings, eliminating the need for older larger displacement engines in some applications.
The VGT actuator moves either vanes or a sliding sleeve inside the turbocharger which increases or decreases exhaust gases driving the turbine wheel, which in turn, increases or decreases turbo boost based on engine operating conditions.
These new VGTs are more complex than older wastegate turbochargers and technicians must be trained to accurately diagnose and repair them. An online resource like Mitchell1 Truck Series is an invaluable tool for techs to access the latest repair and diagnostic information to maintain, diagnose and repair these newer components.
For instance, using the Cummins ISX15 as an example, some of the procedures for maintaining the turbocharger include:
- Inspecting variable geometry actuator and mechanism for proper operation
- Checking axial movement of turbocharger wheels and shaft
- Checking radial movement of turbocharger wheels and shaft
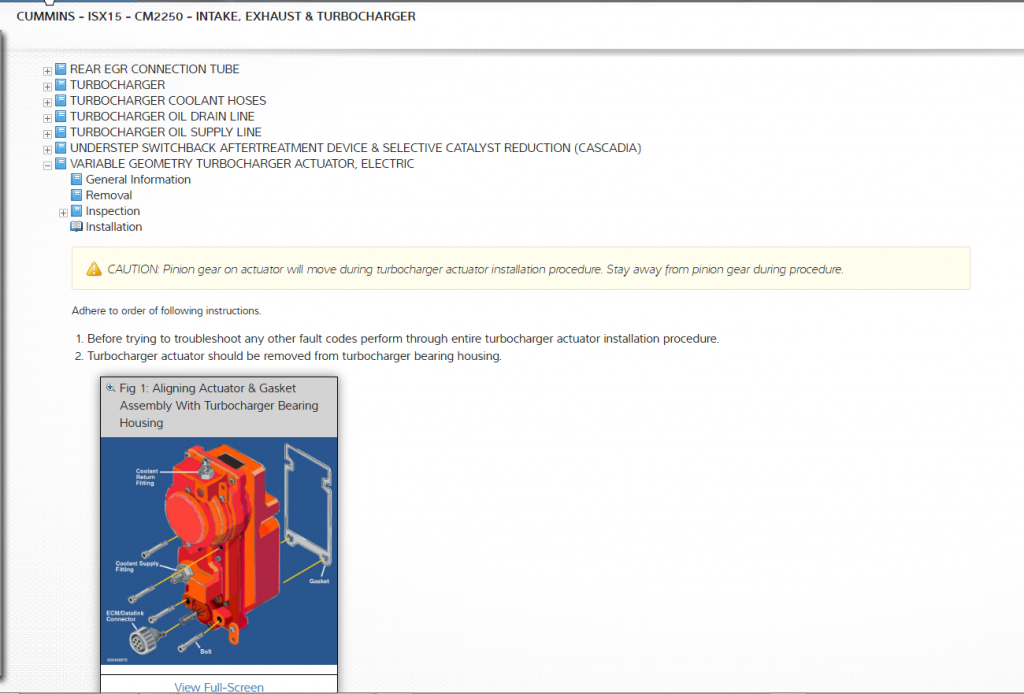
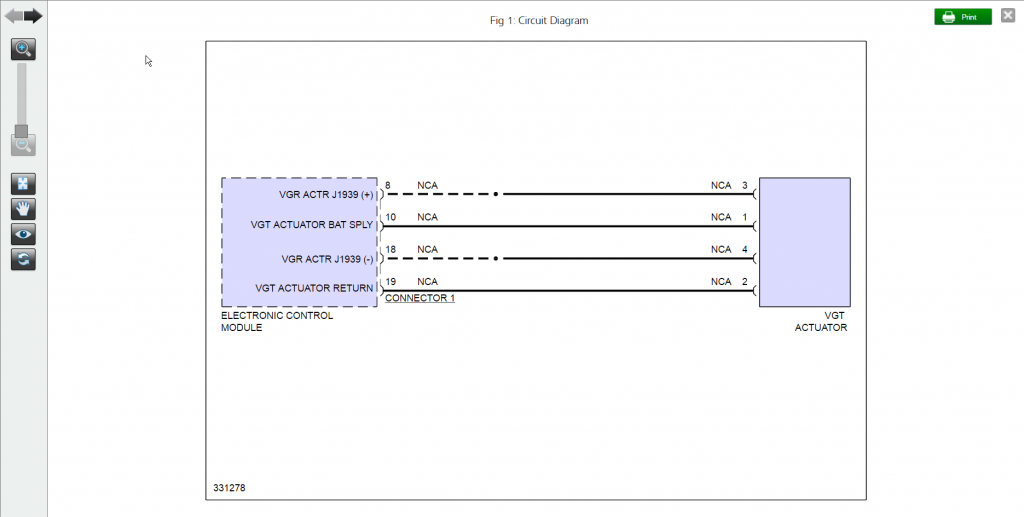
- Calibrating turbocharger actuator to turbo charger (See Figure 2 – click images to expand to full size)
Regular service is always a crucial element in maintaining VGT performance within standards. Some maintenance items to keep in mind are:
- Regular engine oil changes
- Regular coolant flushes
- Inspecting for air leaks in the intake system
- Inspecting for exhaust leaks
- Insuring proper aftertreatment system function
Resources like Mitchell 1 TruckSeries provide information and procedures to properly maintain and service your VGT (See Figures 3-5). Having the information tailored to the code and truck specific to your current application saves you valuable time by eliminating the need to filter through unneeded information.
- Learn more about TruckSeries